Merger and enhancement: the SCO allowed the market to merge with BRICS

The SCO and BRICS markets may merge, the secretariat of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization told Izvestia. They clarified that such a decision should be made at the level of the competent authorities of the member countries of both structures. But we must understand that it will not be possible to quickly unite the markets: this is hindered, among other things, by the participation of states in other organizations, experts say. In the future, a common trading space can help countries cope with the consequences of the harsh US tariff policy and accelerate de-dollarization. Whether such an association is capable of becoming an alternative to the WTO is discussed in the Izvestia article.
Can the SCO and BRICS markets unite
Over time, the SCO and BRICS markets could merge. These organizations have similar goals and objectives aimed at contributing to the prosperity and well-being of the peoples of the participating countries.
— In this regard, the possibility of combining the SCO and BRICS markets is not excluded in the future, but this is a decision of the competent authorities of the respective countries. Currently, the SCO does not have on its agenda the issue of discussing common tariffs and other economic preferences for the countries of the two associations. Again, the decision rests with the leadership of our states," the SCO secretariat told Izvestia.
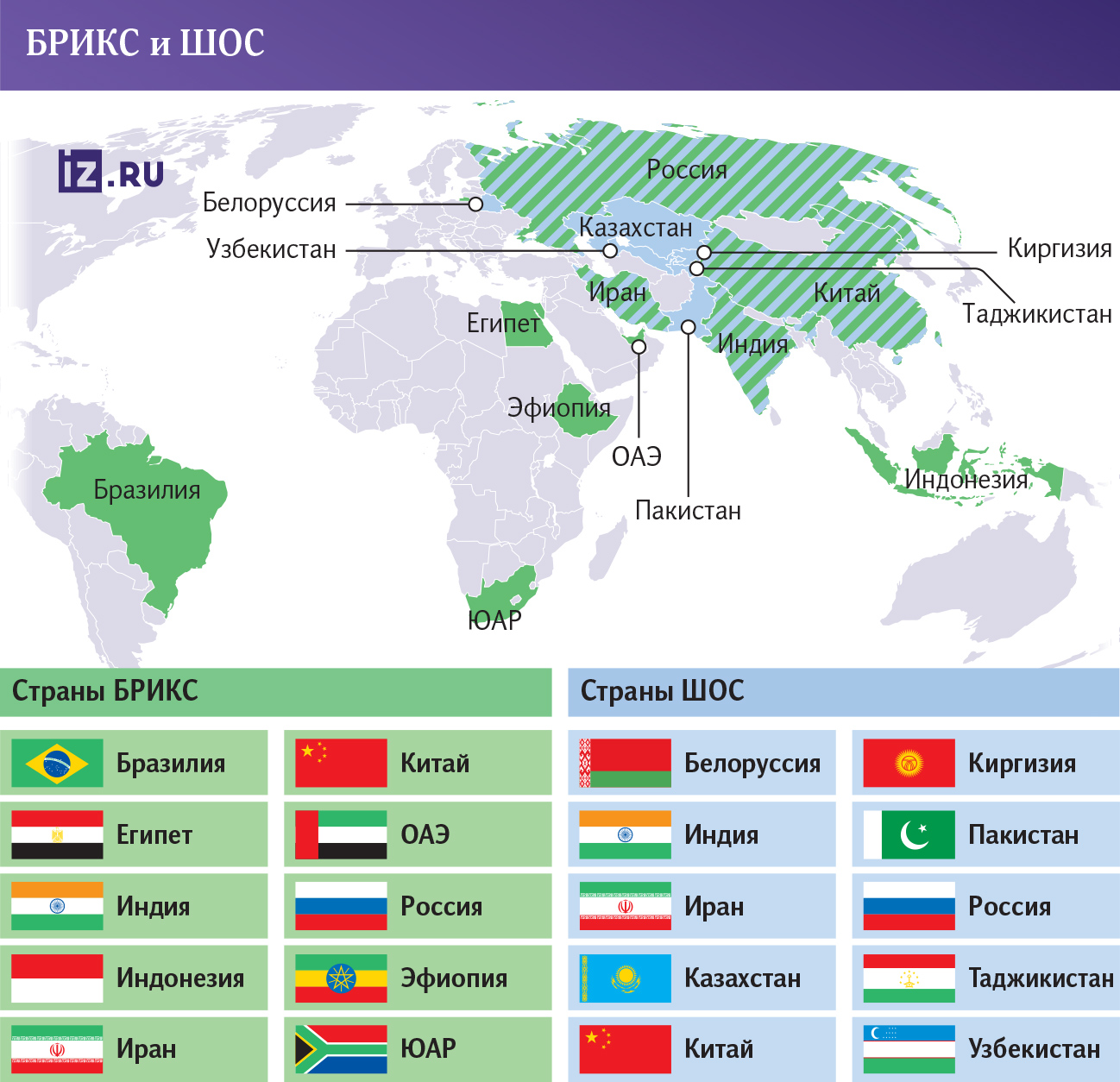
Both associations cover a very wide geography, despite the fact that a number of member countries coincide. The SCO includes Belarus, Russia, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, China, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Pakistan and Iran. Two more countries have observer status — Mongolia and de jure Afghanistan. After the Taliban came to power (the organization is under UN sanctions), the country's participation in SCO meetings has actually been frozen. In addition, the SCO has 14 dialogue partners.
Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, the United Arab Emirates, Iran, Ethiopia, Egypt and Indonesia are full members of the BRICS. In this regard, the unification of markets would mean great opportunities for the development of trade between the countries. Nevertheless, there are significant obstacles to this.
— The SCO and BRICS are initially very different structures. If BRICS is a forum that unites countries from all over the world with common views on the future of the global economy, then the SCO is an organization mainly dealing with security issues," says Kirill Babaev, director of the ICSA RAS.
Although the SCO also has a strong economic component, the expert notes. For example, Zhang Ming, while still secretary general of the organization, told Izvestia in an interview that the main goal in this area is the transition to the free movement of goods, capital, technologies and services in the SCO countries. Moreover, both associations have long been thinking about creating a single payment system, and both structures continue to work on increasing the share of national currencies in mutual settlements.
Obstacles may arise at the institutional level. Neither the BRICS nor the SCO represent an integration association.: As a result, each of the structures does not have its own common market, such as the EAEU and the European Union, said Alexander Korolev, Deputy Director of the Central Research Institute of Higher School of Economics. On the other hand, the BRICS organization's lack of a charter does not make it invisible. On the contrary, the association has been expanding for the second year in a row. And in 2024, following the results of the summit in Kazan, it was also expanded with the category of partner states. Brazil, which holds the BRICS presidency this year, has identified institutional strengthening of the bloc as one of its priorities against the background of the involvement of partner countries. In addition, many experts are unanimous in the opinion that after several years of active expansion of the BRICS, now is the time to work on creating a secretariat and a charter for the association, which the SCO also has.
So far, if it is not possible to conclude international agreements, you can start with a memorandum, for example, a memorandum of understanding or a communique following the summit. It is also important to take into account that the BRICS and SCO members are also members of other organizations. This complicates the process of market integration.
— Not all countries are members of the WTO. For example, Iran, which joined both the BRICS and the SCO. Thus, the countries belonging to both associations have different tariff duties and different participation in free trade zone systems. In addition, most states have a protectionist economy within their associations. For example, India, fearing to open its market, is in no hurry to conclude an agreement with the EAEU from the FTA," says Alexander Korolev.
Brazil, for example, is a member of the MERCOSUR regional economic bloc. Given that MERCOSUR recently agreed with the EU to create a free trade area, cooperation with this organization will be a priority for Brasilia.
Advantages of merging the SCO and BRICS markets
The economic interests of the SCO and BRICS are united at least by the desire for de-dollarization. This will make the countries of both associations less dependent on the G7 states, primarily on the United States, which uses the dollar as a political weapon. Thus, the banks of the BRICS and SCO countries will be less dependent on Washington and its sanctions policy, especially if it comes to market unification.
BRICS is already showing positive growth dynamics. The share of the countries of the association in terms of purchasing power parity in the global economy by the end of 2024 was 36.7%, which is higher than the share of the G7 countries, Vladimir Putin noted at the summit in Kazan. Natalia Milchakova, a leading analyst at Freedom Finance Global, draws attention to the fact that the GDP of the SCO countries accounted for approximately 25% of global GDP, but mainly at the expense of those countries that are simultaneously members of the BRICS — China, India and Russia. In total, the BRICS and non-SCO countries together accounted for about 40% of global GDP in 2024, the expert says.
The Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation estimated the mutual trade turnover between the BRICS countries at $678 billion per year.
"If we add more countries that are members of the SCO but not BRICS, then, according to our estimates, the total trade turnover will grow by at least 35-40%," Natalia Milchakova said.
Against the background of the tough US tariff policy towards many countries, increased economic cooperation within the BRICS and a potential increase in the market at the expense of the SCO countries could help overcome the consequences of restrictions from Washington, independent expert Andrei Barkhota emphasizes.
— China is the main beneficiary of removing barriers within the BRICS and SCO. The potential for an increase in trade turnover in this case does not exceed 20%. But in the wake of the hysteria over the actions of President Donald Trump, the BRICS can really get a new impetus for development. Nevertheless, the absence of the EU and the USA in the associations will not allow the BRICS and the SCO to replace the WTO," Andrei Barkhota believes.
On April 2, Donald Trump announced that he would set a base rate of duties on imported goods at 10%, but in general it varies — for example, the tariff against China was 34%. In response, Beijing has been imposing retaliatory duties of 34% on all products imported from the United States since April 10. This measure will have a serious impact on the economies of both countries, given that the trade turnover between China and the United States reached an impressive $688.28 billion by the end of 2024.
The first stage for the start of cooperation between the BRICS and the SCO may be the development of a plan for cooperation and exchange of information, as well as experience in the field of ecology, said Victoria Panova, Vice Rector of the Higher School of Economics and head of the BRICS Expert Council.
"These can include adaptation and mitigation of the effects of climate change, the implementation of joint projects for the conservation of biological diversity, waste management and environmental protection, assistance in attracting investments and financing projects and programs in the field of environmental protection, the introduction of new environmentally friendly technologies," said Victoria Panova.
In the field of green finance, associations could develop mechanisms to provide tax incentives, stimulate the issuance of green bonds, and measures to improve the credit rating of issuers. On the part of the SCO, the Business Council and the Interbank Association of the organization could take up this task, and on the part of the BRICS, green funds, information platforms on green financing for businesses and NGOs, Victoria Panova summarized.
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»








